Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation Protocol⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the total hip replacement rehabilitation protocol, outlining the different phases of recovery, exercises, precautions, and tips for a successful outcome. It is designed to help patients understand the process, set realistic goals, and actively participate in their rehabilitation journey. This protocol aims to empower individuals to regain mobility, strength, and function following total hip replacement surgery.
Introduction
A total hip replacement, also known as total hip arthroplasty (THA), is a surgical procedure that replaces a damaged hip joint with an artificial one. This procedure is commonly performed to alleviate pain and improve mobility in individuals suffering from severe osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or other conditions affecting the hip joint. The success of a total hip replacement goes beyond the surgery itself; it relies heavily on a structured and comprehensive rehabilitation program that guides patients through the recovery process, restoring their function and enabling them to return to an active lifestyle.
This rehabilitation protocol serves as a roadmap for patients undergoing total hip replacement, outlining the various stages of recovery, exercises, precautions, and essential information for a smooth and effective rehabilitation journey. It emphasizes the importance of active patient participation, tailored exercises, and adherence to specific guidelines to maximize the benefits of the surgery and achieve optimal long-term outcomes. By following this protocol, individuals can regain strength, flexibility, and confidence, ultimately leading to a better quality of life.
Understanding Total Hip Replacement
Total hip replacement involves replacing the damaged ball-and-socket joint of the hip with artificial components. The ball portion, called the femoral head, is replaced with a metal ball attached to a stem that fits into the thighbone (femur). The socket portion, called the acetabulum, is replaced with a metal cup lined with a smooth, durable material, usually plastic or ceramic. These artificial components work together to create a new, functional hip joint.
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves several steps, including⁚
- Preparing the bone⁚ The damaged bone surfaces are carefully prepared to receive the artificial components.
- Inserting the components⁚ The femoral stem is secured into the femur, and the acetabular cup is fitted into the pelvis.
- Securing the components⁚ The components may be cemented into place or secured using a press-fit technique, depending on the patient’s individual needs and the surgeon’s preference.
Total hip replacement is a highly successful procedure, offering significant pain relief and improved mobility for many individuals. However, it’s essential to understand that rehabilitation plays a critical role in optimizing outcomes and ensuring a smooth recovery.
Rehabilitation Goals and Phases
Total hip replacement rehabilitation aims to restore your mobility, strength, and function after surgery. The goal is to regain independence in daily activities and improve your quality of life. This comprehensive process is typically divided into four phases, each focusing on specific objectives and activities. The phases are⁚
- Phase 1⁚ Immediate Post-Operative (0-2 Weeks)
- Phase 2⁚ Early Rehabilitation (2-6 Weeks)
- Phase 3⁚ Intermediate Rehabilitation (6-12 Weeks)
- Phase 4⁚ Advanced Rehabilitation (12+ Weeks)
While the timeframes may vary slightly depending on individual factors and the surgical approach used, these phases provide a general framework for your rehabilitation journey. Each phase builds upon the previous one, gradually increasing the intensity and complexity of exercises and activities. A physical therapist will work closely with you throughout these phases, providing guidance, supervision, and personalized exercise programs to help you achieve your rehabilitation goals.
Phase 1⁚ Immediate Post-Operative (0-2 Weeks)

The immediate post-operative phase focuses on pain management, wound healing, and regaining basic mobility. It is crucial to follow your surgeon’s instructions carefully and adhere to the prescribed pain medications. You will likely be encouraged to start moving your leg and ankle as soon as possible to prevent stiffness and blood clots. This phase often involves⁚
- Pain Management⁚ Pain medications will be provided to manage discomfort and promote healing.
- Deep Breathing and Coughing Exercises⁚ These exercises help prevent pneumonia and improve lung function.
- Ankle Pumps and Foot Circles⁚ These simple exercises help improve circulation and prevent blood clots.
- Gentle Leg Raises⁚ These exercises help strengthen the muscles around your hip and promote range of motion.
- Walking with Assistive Devices⁚ You will start with short walks using a walker or crutches to regain balance and stability.
Phase 1 sets the foundation for your recovery. It is a time for rest, healing, and gradual re-engagement with movement. Your physical therapist will work with you to assess your progress and adjust the exercises as needed.
Phase 2⁚ Early Rehabilitation (2-6 Weeks)
Phase 2 focuses on increasing your range of motion, strengthening the muscles surrounding your hip, and improving your balance and coordination. This phase aims to prepare you for more challenging activities and a gradual return to daily living. Your physical therapist will guide you through a personalized program that may include⁚
- Increased Range of Motion Exercises⁚ You will perform exercises to improve the flexibility of your hip joint, such as hip flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation.
- Strengthening Exercises⁚ You will start with gentle exercises to build strength in your leg muscles, including quadriceps, hamstrings, and gluteal muscles.
- Balance and Coordination Exercises⁚ You will work on improving your balance and coordination, such as standing on one leg, walking on uneven surfaces, and performing heel-toe walking.
- Stair Training⁚ You will learn how to safely navigate stairs with proper technique and assistive devices.
- Functional Activities⁚ You will begin incorporating activities of daily living into your rehabilitation program, such as getting in and out of a car, dressing, and showering.
As you progress through Phase 2, your reliance on assistive devices will gradually decrease. You will begin to participate in more challenging activities, building confidence and independence. Your physical therapist will monitor your progress and adjust the exercises as needed.
Phase 3⁚ Intermediate Rehabilitation (6-12 Weeks)
Phase 3 marks a significant step towards regaining full functional independence. During this phase, the focus shifts towards strengthening and endurance training, while continuing to refine your movement patterns and coordination. Your physical therapist will continue to guide you through a tailored program that may include⁚
- Advanced Strengthening Exercises⁚ You will progress to more challenging exercises that target the muscles surrounding your hip, including squats, lunges, and hip abductor exercises.
- Endurance Training⁚ You will begin to incorporate cardiovascular exercises, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, to improve your overall fitness and stamina.
- Functional Activities⁚ You will continue to practice activities of daily living, but with increased complexity, such as walking longer distances, climbing stairs without assistance, and participating in recreational activities.
- Proprioceptive Exercises⁚ You will engage in exercises that challenge your balance and coordination, such as standing on unstable surfaces or performing exercises with closed eyes.
As you progress through Phase 3, you will notice a significant improvement in your mobility, strength, and endurance. You will be able to participate in more activities and enjoy a higher level of independence. Your physical therapist will continue to monitor your progress and provide guidance as you transition to Phase 4.
Phase 4⁚ Advanced Rehabilitation (12+ Weeks)
Phase 4 marks the final stage of your rehabilitation journey, focusing on optimizing your functional capacity and returning to your desired activity level. This phase emphasizes continued strengthening, endurance training, and functional exercises, tailored to your individual goals and limitations. Your physical therapist will work with you to⁚
- Maximize Strength and Power⁚ You will continue to progress your strengthening exercises, focusing on increasing both strength and power. This may involve incorporating heavier weights, resistance bands, or advanced exercises that challenge your muscles.
- Enhance Endurance⁚ You will continue to engage in cardiovascular exercises, gradually increasing the intensity and duration of your workouts. The goal is to build stamina and improve your overall fitness.
- Return to Functional Activities⁚ You will progress towards your desired activity level, working with your physical therapist to gradually reintroduce activities that you enjoy, such as sports, dancing, or gardening.
- Develop a Home Exercise Program⁚ You will learn a home exercise program to maintain your strength, flexibility, and endurance. This will help you continue to progress even after you have completed formal rehabilitation.
Phase 4 is an ongoing process, and your physical therapist will continue to monitor your progress and make adjustments to your program as needed. The goal is to help you achieve your full functional potential and live a fulfilling and active life.
Home Exercise Program
A home exercise program is an essential part of your recovery after total hip replacement. It helps to maintain the strength, flexibility, and endurance you gained during formal rehabilitation. Your physical therapist will design a personalized program tailored to your individual needs and goals. Here are some common exercises that may be included⁚
- Hip Flexor Stretches⁚ These exercises help to improve the flexibility of the muscles at the front of your hip, which can become tight after surgery.
- Quadriceps Strengthening⁚ Strengthening your quadriceps (front thigh muscles) is crucial for stability and balance. Exercises include straight-leg raises and knee extensions.
- Hamstring Strengthening⁚ Strengthening your hamstrings (back thigh muscles) helps to improve hip extension and control. Exercises include hamstring curls and bridges.
- Glute Strengthening⁚ Strengthening your glutes (buttocks muscles) is important for hip stability and power. Exercises include hip thrusts and squats.
- Calf Strengthening⁚ Strengthening your calf muscles helps to improve ankle stability and power. Exercises include calf raises and heel drops.
It is important to perform your home exercises regularly, as directed by your physical therapist. Listen to your body and stop if you experience any pain. Consistency is key to achieving long-term success in your rehabilitation.
Common Precautions and Restrictions
After total hip replacement surgery, there are important precautions and restrictions you need to follow to protect your new joint and ensure optimal healing. These guidelines typically last for several weeks or months, depending on your individual recovery progress. Here are some common precautions⁚
- Hip Flexion⁚ Avoid bending your hip past 90 degrees for the first few months. This means you should not sit in low chairs, get into a bathtub, or cross your legs.
- Hip Adduction⁚ Avoid crossing your legs or bringing your operated leg across your body.
- Hip Rotation⁚ Avoid twisting or rotating your hip. This includes pivoting on your operated leg or turning your body while keeping your feet fixed.
- Weight-Bearing⁚ Follow your surgeon’s instructions regarding weight-bearing restrictions. You may be advised to use crutches, a walker, or a cane for a period of time.
- Activities⁚ Avoid high-impact activities, such as running, jumping, or contact sports, until your surgeon clears you.
These precautions are designed to prevent dislocation of your new hip joint. It is essential to follow them diligently, as even a minor slip-up could lead to serious complications. Your physical therapist will provide you with specific instructions and modifications as you progress through your recovery.
Pain Management
Pain management is an important aspect of total hip replacement rehabilitation. It is crucial to address pain effectively to facilitate movement, encourage participation in exercises, and promote overall recovery. Your healthcare team will work with you to develop a personalized pain management plan that may include⁚
- Medications⁚ Pain medications, such as over-the-counter analgesics, prescription pain relievers, or anti-inflammatory drugs, may be prescribed to help manage pain.
- Ice Therapy⁚ Applying ice to the surgical site can help reduce swelling and pain.
- Heat Therapy⁚ Warm compresses or heat therapy may be used to relax muscles and alleviate pain.
- Physical Therapy⁚ Physical therapy exercises can help improve range of motion, strengthen muscles, and reduce pain.
- Nerve Blocks⁚ In some cases, your surgeon may recommend a nerve block to numb the area around the hip joint and provide pain relief.
It is essential to communicate openly with your healthcare team about your pain levels and any changes you experience. They can adjust your pain management plan as needed to ensure you have adequate relief and can effectively participate in your rehabilitation program.
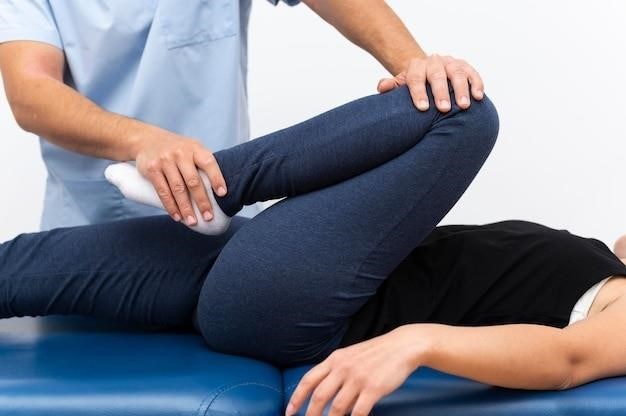
Activities to Avoid
Following total hip replacement surgery, it is crucial to avoid certain activities that could put excessive stress on the new joint and potentially cause complications. These restrictions are typically in place for several weeks or months after surgery, depending on your individual recovery progress; Here are some common activities to avoid⁚
- High-Impact Activities⁚ Avoid activities that involve jumping, running, or high-impact movements, such as jogging, basketball, or tennis.
- Crossing Your Legs⁚ Crossing your legs can cause your hip to rotate inward, which can put stress on the new joint.
- Bending Over 90 Degrees⁚ Avoid bending at the waist beyond 90 degrees, as this can strain the hip joint.
- Twisting or Pivoting⁚ Avoid twisting or pivoting your hip, especially when getting in and out of a car or turning in bed.
- Heavy Lifting⁚ Refrain from lifting heavy objects that could put strain on your hip.
- Certain Exercises⁚ Some exercises, such as leg presses or hamstring curls, may need to be avoided or modified until your hip has healed sufficiently.
Your healthcare team will provide specific instructions on activities to avoid and when you can gradually reintroduce them into your routine. Always follow their guidance to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
Tips for Successful Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after total hip replacement is a journey that requires dedication and patience. While your physical therapist will guide you through exercises and activities, there are several tips you can follow to enhance your recovery and maximize your results. Here are some key points to keep in mind⁚
- Stay Active⁚ Regular exercise is crucial for regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion in your hip. Follow your therapist’s instructions and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
- Follow Your Precautions⁚ It’s essential to adhere to the precautions your surgeon and physical therapist have outlined. Avoiding certain movements and activities can prevent complications and ensure proper healing.
- Listen to Your Body⁚ Pay attention to any pain or discomfort you experience during your exercises. If something feels too intense or uncomfortable, stop and consult with your physical therapist.
- Set Realistic Goals⁚ Don’t expect to recover overnight. Set achievable goals for yourself and celebrate your progress along the way. Be patient with yourself and understand that recovery takes time.
- Seek Support⁚ Lean on your support system for encouragement and assistance. Family, friends, and your healthcare team can provide valuable support during your recovery.
- Stay Positive⁚ Maintain a positive attitude and focus on the progress you’re making. A positive mindset can contribute significantly to your recovery.
By following these tips and working closely with your healthcare team, you can increase your chances of a successful rehabilitation and return to a fulfilling and active lifestyle.
Total hip replacement rehabilitation is a structured process that aims to restore mobility, strength, and function following surgery. It involves a combination of physical therapy, home exercise programs, and lifestyle modifications. By diligently following your healthcare team’s instructions, participating in prescribed exercises, and embracing a positive outlook, you can significantly enhance your recovery and achieve optimal outcomes. Remember that rehabilitation is a journey, and consistency, patience, and a commitment to your recovery are key to regaining your independence and enjoying an active lifestyle. While there may be challenges along the way, the rewards of successful rehabilitation are well worth the effort.
As you progress through your rehabilitation, focus on building a strong foundation for your future. Remember to prioritize your health, embrace a healthy lifestyle, and continue to engage in activities that bring you joy and fulfillment. With dedication and the support of your healthcare team, you can successfully navigate your recovery and achieve a positive and lasting impact on your overall well-being.