Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy CPT Codes⁚ An Overview
CPT codes 19083 and 19084 are used for ultrasound-guided breast biopsies․ Code 19083 is for the first lesion biopsied, while 19084 is an add-on code for each additional lesion․ These codes encompass percutaneous tissue sampling under ultrasound guidance, potentially including placement of localization devices and imaging of specimens․ Accurate coding is crucial for appropriate reimbursement․
CPT Codes 19083 and 19084
The primary CPT codes utilized for ultrasound-guided breast biopsies are 19083 and 19084․ Code 19083 specifically addresses the first lesion biopsied during the procedure․ This code encompasses the entire process, from initial ultrasound guidance and percutaneous needle insertion to the collection and imaging of the tissue sample․ Importantly, it also includes the use of breast localization devices if those were implemented during the biopsy․ Code 19084, on the other hand, serves as an add-on code․ It is used to bill for each additional lesion biopsied beyond the initial one reported under code 19083․ Therefore, if multiple suspicious areas are identified and biopsied during a single procedure, both 19083 and 19084 will be used in the billing process, reflecting the complexity and extent of the intervention․ Careful adherence to these specific codes is essential for correct medical billing and reimbursement․
First Lesion vs․ Additional Lesions
Differentiating between the first lesion biopsied and subsequent additional lesions is critical for accurate CPT code assignment in ultrasound-guided breast biopsies․ CPT code 19083 is exclusively for the initial lesion targeted and biopsied․ This code encompasses the complete procedural steps involved in obtaining a sample from that specific location, including ultrasound guidance, needle insertion, tissue acquisition, and potential imaging of the excised specimen․ If only one suspicious area is identified and biopsied, only code 19083 is reported․ However, if multiple lesions require biopsy, the process becomes more complex․ Each additional lesion biopsied beyond the first one necessitates the use of the add-on code, 19084․ This add-on code is appended to code 19083, reflecting the increased procedural work involved in targeting and sampling multiple sites․ Proper distinction between the initial and subsequent lesions ensures accurate billing and appropriate reimbursement for the complete scope of the procedure․
Understanding the Procedure
Ultrasound-guided breast biopsy involves using real-time ultrasound imaging to precisely guide a needle into a suspicious breast lesion․ The procedure typically begins with the radiologist carefully locating the abnormality using ultrasound․ Once the target is identified, a small incision or puncture is made in the skin․ A specialized needle is then advanced under ultrasound guidance, extracting a tissue sample from the lesion․ The size and number of samples obtained depend on the size and characteristics of the lesion․ The entire procedure is conducted under sterile conditions to minimize infection risk․ After the biopsy is completed, the needle is removed, and pressure is applied to the site to control bleeding․ A small bandage is usually placed over the puncture site․ The extracted tissue samples are then sent to a pathology laboratory for analysis․ The results of the pathology analysis are crucial in determining the nature of the lesion and guiding further treatment plans․
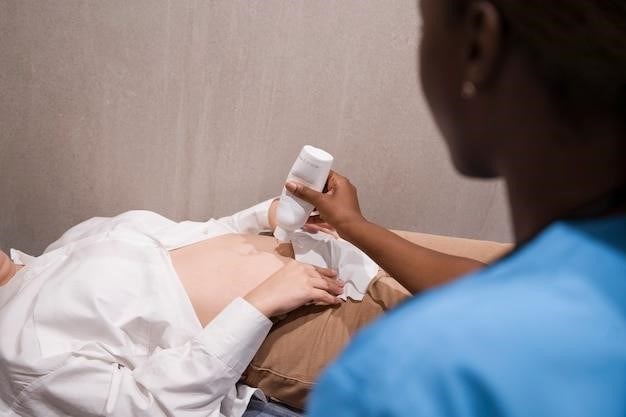
Imaging Guidance in Breast Biopsy
Accurate localization of breast lesions is critical for biopsy procedures․ Ultrasound, alongside other modalities like mammography, MRI, and CT, provides real-time imaging guidance, ensuring precise needle placement and optimal tissue sampling for diagnosis․
Ultrasound Guidance vs․ Other Methods
Ultrasound guidance for breast biopsy offers several advantages over other imaging modalities․ Its real-time imaging capabilities allow for dynamic visualization of the needle and lesion throughout the procedure, ensuring accurate targeting and minimizing trauma․ Unlike mammography or tomosynthesis, which provide static images, ultrasound allows for immediate adjustments in needle position as needed, enhancing precision․ Furthermore, ultrasound is readily available, relatively cost-effective, and doesn’t involve ionizing radiation, making it a safe and practical choice for many patients․ While other methods like stereotactic biopsy (using mammography or tomosynthesis) or MRI-guided biopsy offer advantages in specific situations (e․g․, non-palpable lesions), ultrasound’s versatility and accessibility make it a widely used technique for breast biopsy procedures․ The choice of imaging modality often depends on lesion characteristics, patient factors, and the capabilities of the facility performing the biopsy․ The selection of the appropriate imaging guidance method is crucial for ensuring the safety and success of the breast biopsy procedure, directly impacting diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes․ The use of various imaging techniques for breast biopsy is a continually evolving field, with ongoing research and technological advancements shaping best practices․
Codes for Different Imaging Modalities
While CPT codes 19083 and 19084 specifically apply to ultrasound-guided breast biopsies, other codes exist for procedures utilizing different imaging modalities․ For instance, procedures guided by fluoroscopy may use codes such as 10007 and 10008 (though note these are out of numeric sequence in the CPT manual and require careful review)․ Similarly, CT-guided biopsies may have distinct codes (like 10009 and 10010), and MRI-guided procedures may utilize codes such as 10011 and 10012․ The specific code used depends entirely on the imaging modality employed to guide the needle placement during the biopsy․ It’s crucial to consult the most current CPT codebook and relevant coding guidelines to ensure accurate reporting based on the specific imaging technique used in each individual case․ Incorrect coding can lead to claim denials or delays in reimbursement․ Therefore, thorough understanding of the various codes associated with different imaging modalities is essential for proper medical billing and coding practices․ Staying updated with CPT code changes and associated guidelines is vital for healthcare providers to maintain accurate billing and avoid potential financial repercussions․
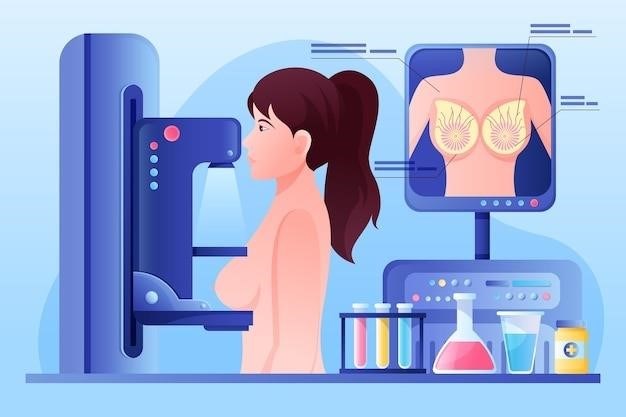

Additional CPT Codes and Considerations
Beyond the primary codes (19083 and 19084), additional codes might apply depending on factors such as the placement of localization devices or imaging of biopsy specimens․ Modifier usage also plays a critical role in accurate coding․
Add-on Codes and Modifiers
The accurate application of add-on codes and modifiers is essential for precise billing in ultrasound-guided breast biopsies․ While CPT codes 19083 and 19084 address the core procedure, additional codes may be necessary to reflect ancillary services․ For instance, if a localization wire or clip is placed during the biopsy, a separate code should be appended to capture this additional step, ensuring complete and accurate reimbursement for all services rendered․ Modifiers are crucial for specifying circumstances like multiple lesions, different locations (e․g․, separate lesions in the left and right breast), or if the procedure was performed by multiple physicians․ The appropriate modifier selection prevents coding errors and ensures proper claims processing․ Understanding the nuances of add-on codes and modifiers is paramount for compliant and complete medical billing related to ultrasound-guided breast biopsies․ Careful documentation of each step in the procedure and diligent code selection minimize billing denials and facilitate timely payment for healthcare providers․ Always consult the most current CPT codebook and relevant payer guidelines to maintain compliance with billing regulations․ Incorrect coding can lead to financial penalties, and thus, accurate coding practices are a cornerstone of responsible medical billing․
Reporting Multiple Lesions and Procedures
When multiple lesions are biopsied during a single ultrasound-guided breast biopsy procedure, specific coding conventions apply to ensure accurate billing․ The primary code, 19083, covers the first lesion biopsied․ Subsequently, for each additional lesion sampled during the same session, the add-on code 19084 must be reported separately․ This ensures that each lesion is accounted for in the billing process, reflecting the complexity and extent of the procedure․ The number of 19084 codes appended directly corresponds to the number of additional lesions biopsied․ It’s crucial to meticulously document the number of lesions biopsied and their locations within the medical record to support the coding choices․ If, in addition to the breast biopsy, other procedures such as lymph node biopsies or placement of localization devices are undertaken, appropriate separate CPT codes for those individual services should be included in the claim․ Accurate reporting of multiple lesions and procedures avoids coding errors and ensures complete reimbursement while adhering to established medical billing guidelines․ Thorough documentation and correct code application are essential for efficient claims processing and minimize the risk of denials or payment delays․
Accreditation and Resources
The ACR offers accreditation programs for various imaging modalities, including breast ultrasound․ Additional resources and information on coding and billing can be found through professional medical organizations and online databases․ Staying updated on coding guidelines is vital for accurate medical billing;
ACR Accreditation Programs
The American College of Radiology (ACR) plays a significant role in ensuring quality and standardization in medical imaging, including breast ultrasound․ Their accreditation programs are designed to evaluate and recognize facilities that meet rigorous standards for equipment, personnel qualifications, and quality assurance protocols․ Achieving ACR accreditation demonstrates a commitment to providing high-quality patient care and adherence to best practices․ This is particularly important for procedures like ultrasound-guided breast biopsies, where image quality and procedural accuracy are critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning․ The ACR’s accreditation process involves a comprehensive review of the facility’s policies, procedures, and technical capabilities, ensuring that they meet the highest standards of excellence․ Accreditation not only enhances a facility’s reputation but also provides patients with confidence in the quality of care they receive․ For facilities performing ultrasound-guided breast biopsies, ACR accreditation serves as a valuable credential, showcasing their commitment to providing accurate and reliable diagnostic services․
Additional Information and Resources
Beyond the core CPT codes and ACR accreditation, several resources offer valuable information for understanding and navigating the complexities of ultrasound-guided breast biopsies and their associated billing․ The American Medical Association (AMA) website provides the most up-to-date CPT code descriptions and guidelines, crucial for accurate coding and reimbursement․ Professional medical coding organizations offer detailed coding manuals and educational resources to assist healthcare providers in correctly applying CPT codes in various clinical scenarios․ These resources often include examples, case studies, and explanations to clarify complex situations․ Furthermore, various medical journals and online databases contain research articles and clinical studies that offer further insights into the procedure’s technical aspects and clinical implications․ Staying informed through these resources helps healthcare providers stay current on best practices and ensures accurate billing practices․ Regularly reviewing updates from professional organizations and relevant literature is essential for maintaining high standards of care and efficient medical billing․